|
| Filename | Size |
|---|---|
| EffectiveMMP_Model_V2.mph | 3.3 MB |
| Download all files (Zip-archive) | ~ 2.6 MB |
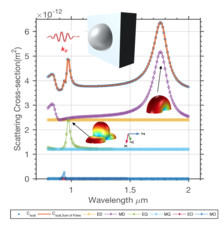
Effective multipole expansion for scattering of particles on a highly conductive substrate
Mike Li, A*STAR
Email:
In this model, we simulate a light wave scatters off a silicon hemisphere on a PEC boundary and decompose the scattering to a set of 'effective multipoles' so that the scattering properties can be understood. This model is a simple extension of the multipole expansion model contributed by Grahn et al (https://www.comsol.com/model/multipole-analysis-of-electromagnetic-scattering-31901). It applies well to a class of problems, where the substrates, which the scattering particle is sitting on or elevated from, can be approximated as a perfect electric conductor. For example, substrates made of gold and silver in the mid-infrared frequencies.
A slight modification of this model can be used to describe scatterers on metallic substrates in the optical frequencies as well. In addition, it works on arbitrary background field, including oblique incidence of light. The derivation of the effective multipole coefficients and the result of this simulation is discussed in the following reference ('Generalized Method of Images and Reflective Color Generation from Ultrathin Multipole Resonators' by S.Q. Li et al, ACS Photonics, 2018. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsphotonics.8b00161). It is applicable to design meta-atoms/nano-antennas for various applications.
Note: For recent version of COMSOL, the wavelength sweep will not work correctly for the second study, as it does not choose the correct wavelength results from the first study automatically. This may be solved by moving the parameter sweep of lambda0 back to the wavelength domain node.
User Comments
|
洋 余 Feb 16, 2019 at 3:45am UTC |
|
Thank you for your model. |
|
Curry James Apr 15, 2019 at 6:30am UTC |
|
thanks |
Login to comment on this entry.
