A Silicon Quantum Dot in a Uniform Magnetic Field
Application ID: 88981
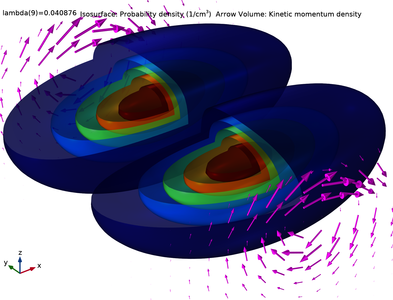
This tutorial model solves a two-component Schrödinger equation for the eigenstates of a simple silicon quantum dot in a uniform magnetic field, based on the paper by Jock et al. on the topic of spin-orbit qubits. The built-in domain condition Lorentz Force for the Schrödinger Equation interface is used to account for the contribution to the kinetic momentum from the vector potential. The coupling of the spin-up and spin-down components is implemented using the built-in domain condition Zeroth Order Hamiltonian. Together with the benchmark model k dot p Method for Strained Wurtzite GaN Band Structure, these examples show how to set up multiple wave-function components with the Schrödinger Equation interface. The computed probability density and kinetic momentum density of the ground state compare well with Supplementary Figure 1 in the paper. In addition, the computed energy difference between the first two eigenstates agrees well with the expected value from an intuitive analytic calculation.
案例中展示的此类问题通常可通过以下产品建模:
您可能需要以下相关模块才能创建并运行这个模型,包括:
建模所需的 COMSOL®产品组合取决于多种因素,包括边界条件、材料属性、物理场接口及零件库,等等。不同模块可能具有相同的特定功能,详情可以查阅技术规格表,推荐您通过免费的试用许可证来确定满足您的建模需求的正确产品组合。如有任何疑问,欢迎咨询COMSOL 销售和技术支持团队,我们会为您提供满意的答复。
