Lithium-Ion Battery Aging with Varying Solvent Composition Effects
Application ID: 140241
The liquid electrolyte in lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) typically consists of a lithium salt, such as LiPF6, dissolved in one or several solvents.
Commercial LIBs commonly employ a mix of multiple hydrocarbon-based solvents along with additional additives. In an electrolyte consisting of multiple solvents, the local electrolyte transport properties within the separator and the electrodes, such as conductivity, may depend not only on the salt concentration but also on the ratio of the different solvents.
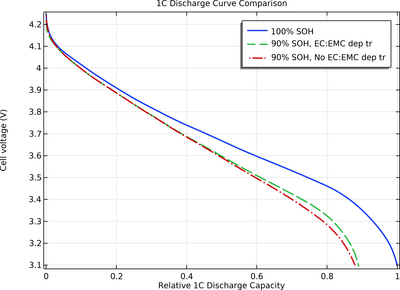
As the battery ages, parasitic reactions may predominantly consume one of the solvents, resulting in a varying ratio of the different solvents over time. This change can, in turn, alter how the electrolyte transport properties are influenced by the local salt concentration in the cell throughout the battery's lifetime.
This tutorial model explores how the consumption of one of the solvents in an aging battery cell impacts its 1C discharge capacity.
To learn more about this model, see our accompanying blog post "The Effects of Varying Solvent Compositions on Lithium-Ion Battery Aging".
案例中展示的此类问题通常可通过以下产品建模:
您可能需要以下相关模块才能创建并运行这个模型,包括:
建模所需的 COMSOL® 产品组合取决于多种因素,包括边界条件、材料属性、物理场接口及零件库,等等。不同模块可能具有相同的特定功能,详情可以查阅技术规格表,推荐您通过免费的试用许可证来确定满足您的建模需求的正确产品组合。如有任何疑问,欢迎咨询 COMSOL 销售和技术支持团队,我们会为您提供满意的答复。
